tree in bud opacities seen in
Originally and still often thought to be specific to endobronchial Tb the sign is actually non-specific and is the manifestation of pus mucus fluid or other. Ground-glass opacities and airspace consolidation correlate with focal or diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage that occurs in approximately 10 of.

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad
No definite tree in bud opacities are seen.
. What does tree-in-bud opacities mean. And branching linear structures so-called tree-in-bud pattern are frequently seen 138143. Mycobacterium avium complex is the most common cause in most series.
2 However the classic cause of tree-in-bud is Mycobacterium tuberculosis especially when it is active and contagious and associated with cavitary lesions. However the most common process leading to this CT appearance is infection. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated.
Commonly its seen with infections like MAC mycobacterium avium complex a chronic but usually benign condition. A tree-in-bud pattern of centrilobular nodules from metastatic disease occurs by two mechanisms. Studies have reported that pulmonary TB accounts for only 28 of the cause of tree-in-bud opacities as opposed to pulmonary apical granulomas and fibrosis being more suspicious of.
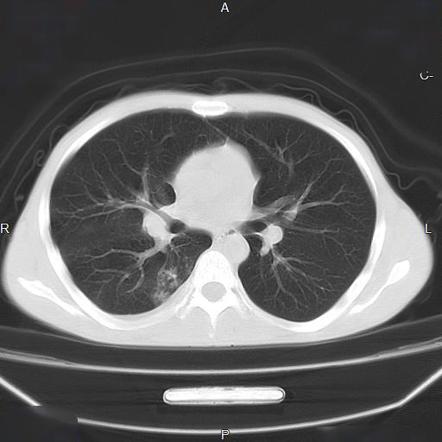
Malignancy can be. Ground glass opacity 639 reticular linear opacities 530 and interlobular septal thickening 205 were frequently identified findings of HRCT among children with DRC and no tree-in-bud pattern was observed Figures 2 3However among children with DRC by M. Uncommonly this pattern can be seen in other entities that cause luminal impaction bronchiolar dilatation or wall thickening including cystic fibrosis immune deficiency inflammatory bowel disease and diffuse panbronchiolitis.
Although initially described in 1993 as a thin-section chest CT finding in active tuberculosis TIB opacities are by. The only new thing on the report states. Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan.
The tree-in-bud pattern indicates disease affecting the small airways. These are due to filling of the distal bronchioles and involvement of the adjacent alveoli most often caused by infectious bronchiolitis bronchitis and aspiration. Correlation with symptoms and attention on follow up to ensure resolution is suggested.
In radiology the tree-in-bud sign is a finding on a CT scan that indicates some degree of airway obstruction. In radiology the tree-in-bud sign is a finding on a CT scan that indicates some degree of airway obstruction. The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly seen at thin-section computed tomography CT of the lungs.
Pneumoniae imaging patterns of HRCT demonstrated a. The differential diagnosis is lengthy. 1 direct filling of the centrilobular arteries by tumor emboli and 2 fibrocellular intimal hyperplasia due to carcinomatous endarteritis.
1 It is important for clinicians to remember that this pattern has an extensive. On HRCT lentil aspiration pneumonia manifests as centrilobular nodules some with a tree-in-bud appearance. The tree-in-bud pattern suggests active and contagious disease especially when associated with adjacent cavitary disease within the lungs.
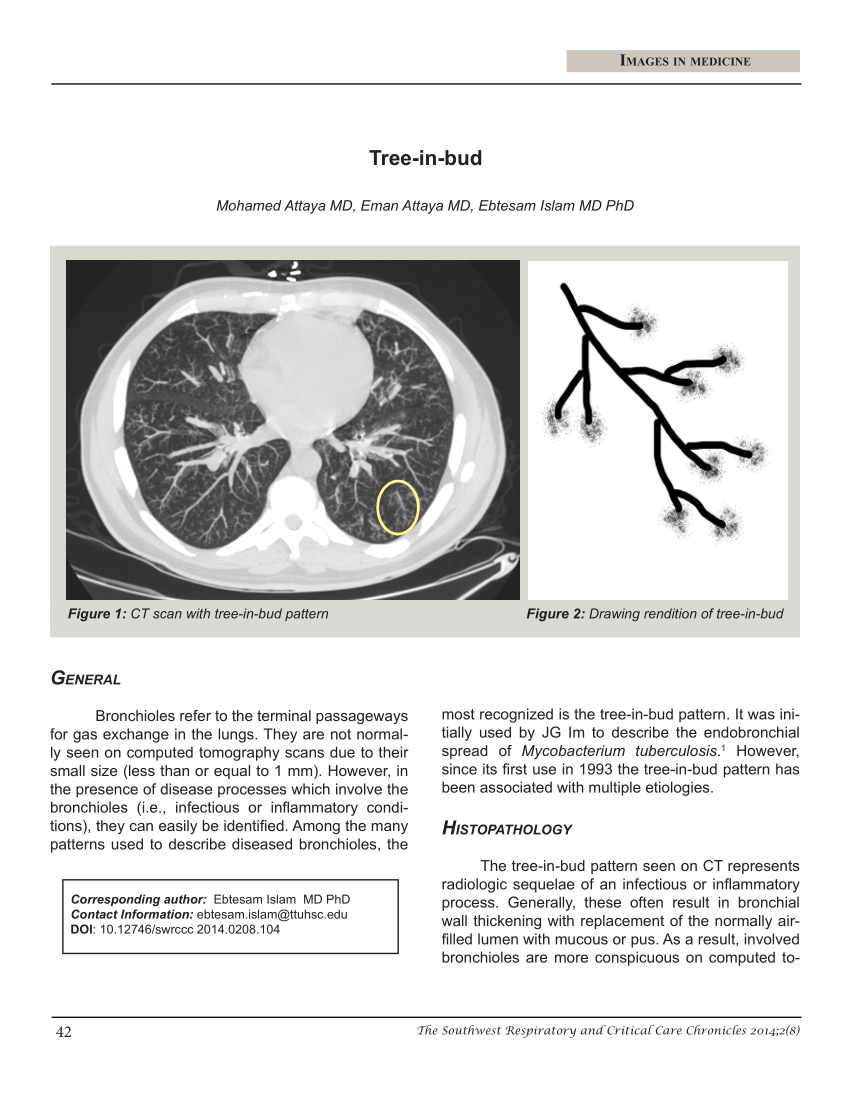
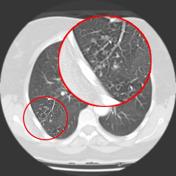
This tree-in-bud pattern is due to the presence of caseation necrosis and granuloma-. Tree-in-bud appearances on CT scans are usually inflammation in the terminal bronchioles and alveoli the very small airways and airspaces. Tree in bud opacification refers to a sign on chest CT where small centrilobular nodules and corresponding small branches simulate the appearance of the end of a branch belonging to a tree that is in bud.
Usually somewhat nodular in appearance the tree-in-bud pattern is generally most pronounced in the lung periphery and associated with abnormalities of the larger airways. Are tree-in-bud nodules cancerous. What does tree-in-bud opacities mean.
However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. TIB opacities represent a normally invisible branches of the bronchiole tree 1 mm in diameter that are severely impacted with mucous pus or fluid with resultant dilatation and budding of the terminal bronchioles 2 mm in diameter1 photo. It consists of small centrilobular nodules of soft-tissue attenuation connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber that originate from a single stalk.
No hilar or mediastinal lymphadenopathy. As in this case renal cell carcinoma is one of the most common malignancies that may produce this vascular cause of tree-in-bud pattern. TIB opacities are also associated with bronchiectasis and small airways obliteration resulting in mosaic air trapping.
Tree-in-bud opacities appear as tiny centrilobular branching structures on CT most often in the lung periphery which resemble budding trees Figure 18-4. 32 rows Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan. Tuberculosis many infectious organisms can produce this pattern.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. School Davao Medical School Foundation. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of causes of TIB opacities and identify patterns of disease associated with TIB opacities.
3 Aspiration is also a common cause of the tree-in-bud formation. The tree-in-bud sign is a nonspecific imaging finding that implies impaction within bronchioles the smallest airway passages in the lung. Course Title DEPARTMENT 164.
There is minor gas trapping within the right upper zone with emphysematous changes evident. 8081 On CT the tree-in-bud pattern manifests as small 24 mm centrilobular well-defined nodules connected to linear branching opacities that. Tree-in-bud refers to a pattern seen on thin-section chest CT in which centrilobular bronchial dilatation and filling by mucus pus or fluid resembles a budding tree.
In radiology the tree-in-bud sign is a finding on a CT scan that indicates some degree of airway obstruction. The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly seen at thin-section computed tomography CT of the lungs. What are tree in bud opacities and in what conditions may they be seen Dilated.
It consists of small centrilobular nodules of soft-tissue attenuation connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber that originate from a single stalk. Although commonly associated with M. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
These small clustered branching and nodular opacities represent terminal airway mucous impaction with adjacent peribronchiolar inflammation. It can be seen with TB and fungal infections as well. There is a new cluster of tree in bud opacities in the right middle love with minimal uptake above background which is almost certainly infectiousinflammatory.
Patterns of Radiological Imaging. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. What are tree in bud opacities and in what conditions.
Pages 85 This preview shows page 29 -. 11 TIB opacities represent a central imag- Background. The most common CT findings are centrilobular nodules and branching linear and nodular opacities.
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Hrct Scan Of The Chest Showing Diffuse Micronodules And Tree In Bud Download Scientific Diagram

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

References In Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Chest

References In Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Chest

Tree In Bud Pattern Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Computed Tomography Of The Chest Showed Nodular Opacities With Tree In Download Scientific Diagram

Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
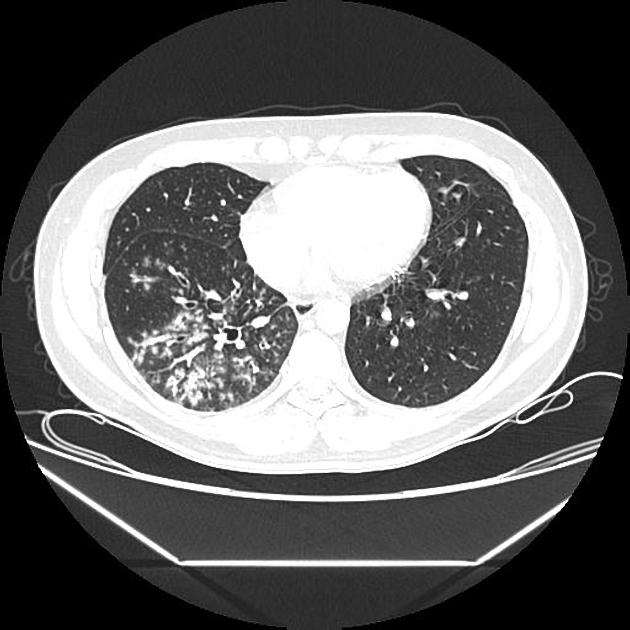
Tree In Bud Appearance Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Pdf Tree In Bud Semantic Scholar

References In Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Chest

Tree In Bud Pattern Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Pdf Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Semantic Scholar